Published on July 22, 2024
– Updated on July 22, 2024
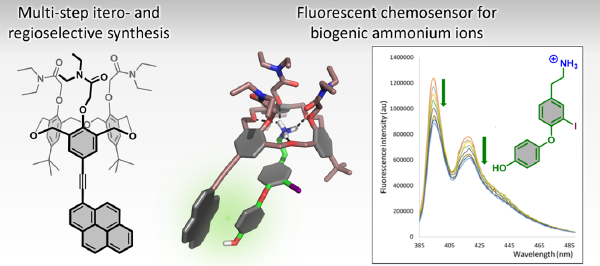
Development of a Cone Homooxacalix[3]arene-based Fluorescent Chemosensor for the Selective Detection of Biogenic Ammonium Ions in Protic Solvents, by Simon Lambert, Romain Carpentier, Martin Lepeintre, Caterina Testa, Andrea Pappalardo, Kristin Bartik & Ivan Jabin - First published: 21 July 2024
Development of a Cone Homooxacalix[3]arene-based Fluorescent Chemosensor for the Selective Detection of Biogenic Ammonium Ions in Protic Solvents,
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.4c01249